CONTACT
We will reply as soon as possible.
Enevia Health, LLC
30 N Gould Ste N, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
The gut microbiota is responsible for a variety of important and vital functions. Among these functions, its role stands out in maintaining the integrity of the intestinal barrier, stimulating the regeneration of the epithelium through the production of short chain fatty acids (SCFA) and other metabolites, promoting mucus production, fermentation of indigestible carbohydrates and other metabolic activities. Furthermore, the intestinal microbiota plays a crucial role in the maturation of the immune system, as well as in the synthesis and metabolism of essential nutrients, and contributes to the elimination of medications.
During fetal development, interactions between the microbiota and the brain can be observed, showing that there is transport of bacteria and their metabolites through the amniotic fluid between the mother and the fetus. After birth, the child is exposed to environmental microorganisms, which begins the process of intestinal colonization. Factors such as the type of delivery (vaginal or cesarean section) and maternal health can affect the initial colonization of the baby's intestine. During early childhood, the composition of the intestinal microbiota will be influenced by the type of breastfeeding (breast or formula), diet, and the use (or abuse) of antibiotics.
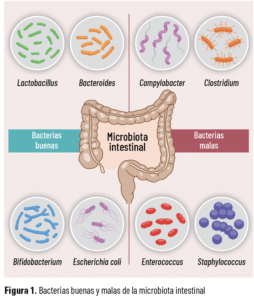
Intestinal dysbiosis refers to a qualitative or quantitative imbalance in the composition of the intestinal microbiota, which implies an increase in pathogenic bacteria, a reduction in beneficial bacteria or modifications in the diversity and distribution of bacteria that inhabit the gastrointestinal tract. When it occurs it can negatively affect intestinal functionality and overall health and has been linked to gastrointestinal and metabolic disorders, as well as autoimmune diseases and neurological conditions such as anxiety, depression and autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
The causes of dysbiosis can be diverse, including environmental and genetic factors. Identifying the underlying cause of dysbiosis is crucial to reversing or improving both gastrointestinal function and overall health.
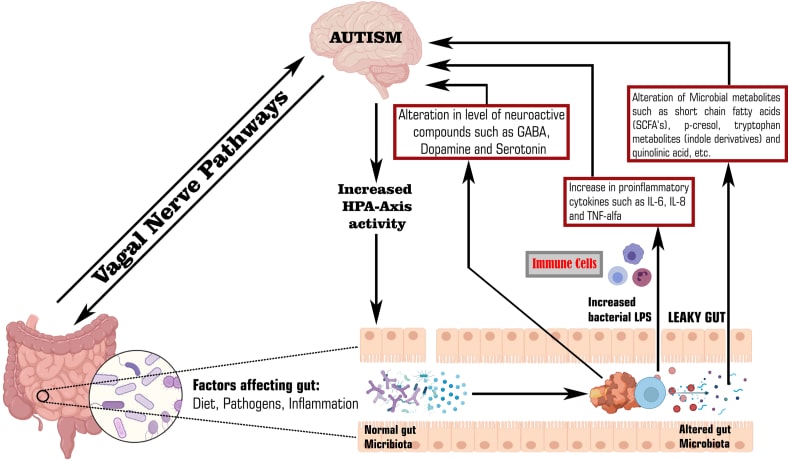
Significant alterations in the intestinal microbiota of individuals with autism spectrum disorder appear to influence the immune system, activating it and triggering the release of chemokines and cytokines that affect the central nervous system through the vagus nerve.
Cytokines include interleukin-1β (IL-1β), IL-6, IL-8, interferon-γ (INF-γ) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), all of which are pro-inflammatory. and that they are part of the innate and adaptive immune response, and that their deregulation could be involved in some inflammatory conditions and/or autoimmune diseases, including neuropsychiatric disorders such as ASD. These proteins are capable of crossing the blood-brain barrier (BBB or Blood-Brain Barrier), thus establishing a connection between intestinal dysbiosis and ASD.
The increased intestinal permeability in ASD, caused by the dysbiosis itself, leads to the intestinal barrier allowing molecules such as toxins, bacteria and metabolic products (Lipopolysaccharides or LPS) to cross the intestinal barrier and enter the blood circulation, triggering a response. systemic inflammatory disease that causes the activation of the immune system with the release of inflammatory cytokines.
That is, dysbiosis can trigger a series of chain events that affect the overall health and well-being of the ASD patient. In this sense, intestinal dysbiosis, by increasing intestinal permeability, creates a pathway for LPS and other toxins to enter the bloodstream. Once in the circulation, these toxins can trigger a cascade of inflammatory events, activating the immune system and promoting the release of proinflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1β, TNF-α and IFN-γ, among others.
This inflammatory response can contribute to the chronicity of inflammation and the disruption of certain organs and systems, increasing the symptoms associated with ASD and the risk of developing other medical problems.
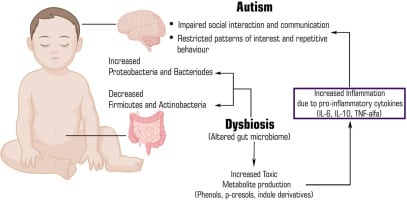
So far, we have observed that gut dysbiosis is linked to changes in overall health. However, to date, it has not been established with certainty whether there is a specific pattern or group of bacteria associated with autism.
Although differences have been observed in the composition of the intestinal microbiota between individuals with autism and without autism. Some microorganisms have been identified that seem to be more or less present in people with autism, such as a high abundance of Proteobacteria, Lactobacillus, Bacteroides, Desulfovibrio, Clostridium, while the levels of Bifidobacterium, Blautia, Dialister, Prevotella, Veillonella and Turicibacter were considerably lower. However, more research is needed to confirm these findings and better understand the contribution of the gut microbiota to the development and manifestation of autism.
In a review study conducted by the Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar in 2022, the impact of the levels of some microbes present in the gut microbiotas of individuals with autism was investigated. The findings were:
The need to address the intestinal microbiota is presented as a therapeutic objective in people with autism, due to its role in both the modulation of the immune system and the production of neurotransmitters and inflammation. Challenges and limitations arise from individual variability in response to treatments and difficulty in selecting specific probiotic strains.
Research has shown positive results from a variety of treatments, such as the use of probiotics, prebiotics, fecal transplantation, microbiota transfer therapy, and dietary changes. Considering microbiota transfer therapy as a modification of fecal transplantation, where antibiotic treatment is first performed, followed by intestinal cleansing, to finally perform a fecal transplant using a high initial dose of human intestinal microbiota.
The exploration and implementation of therapeutic approaches focused on the gut microbiota represent a new vision in the treatment of ASD, with the aim of improving gastrointestinal symptoms, immune function, inflammation and possibly behavioral and cognitive symptoms of ASD. This offers hope for improvement in the quality of life of people with this disorder.
These therapies are based on the understanding of the role that the intestinal microbiota plays in the pathophysiology of ASD and consist of interventions that are aimed at repairing or modifying the intestinal microbiota, seeking to correct microbial imbalances that may contribute to the development and manifestation of symptoms. including but not limited to the use of probiotics and prebiotics to promote the increase of beneficial bacteria, fecal transplantation and microbiota transfer therapy to reestablish a healthy intestinal microbiota.
Article written by Enevia Health Collaborator: Loles Marco
Graduated in Human Nutrition and Dietetics.
lolesmarcobermudo@gmail.com
To learn more about this topic, we leave you the link to the previous articles and our Web
We will reply as soon as possible.
30 N Gould Ste N, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Our groups are the ideal platform to learn and share your scientific concerns about neurodevelopment issues
*Our purpose is informational only, it is not intended to be a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
We are working on our website. For any queries, you can contact our customer service team at atencionalcliente@eneviahealth.com